How Do Metal Detectors Work is a question that often piques curiosity. Metal detectors are fascinating devices that have become an integral part of various industries and everyday life. These ingenious instruments are designed to detect the presence of metallic objects hidden beneath the surface or concealed within various materials.
In this concise introduction, we will unravel the basic principles behind their operation. From treasure hunters seeking hidden relics to security personnel safeguarding public spaces, understanding the fundamental mechanics of metal detectors is essential. So, let’s embark on a journey to demystify the technology that enables these devices to uncover the secrets hidden in the world of metals.
Understanding the Basics of Metal Detectors Work
Before we delve into the intricate workings of metal detectors, it’s important to understand their fundamental components and functions.
- Control Box: This is the brain of the metal detector, housing the electronics that manage and regulate the device’s functions. Users can adjust settings, such as sensitivity and discrimination, on the control box.
- Search Coil: The search coil is the part of the detector that makes contact with the ground. It sends and receives signals to detect metal objects in the surrounding area.
- Shaft: The shaft connects the control box to the search coil. It’s typically adjustable to accommodate users of different heights and preferences.
Now, let’s dive deeper into how these components work together to detect metal objects.
How do Metal Detectors work?
At the heart of every metal detector is a concept known as electromagnetic induction. This principle relies on the generation of electromagnetic fields and their interaction with metal objects. Here’s a simplified explanation of how metal detectors use this principle to work their magic:
- Generating an Electromagnetic Field: When you turn on a metal detector, it generates a magnetic field around the search coil. This magnetic field is produced by passing an electric current through a wire coil in the search coil.
- Metal Object Interaction: When the metal detector’s magnetic field encounters a metal object, it induces an electric current within the metal. This electric current generates its magnetic field, opposing the one created by the detector.
- Signal Reception: The metal detector’s search coil also acts as a receiver. It detects the magnetic field generated by the induced current in the metal object. This is similar to how a radio antenna picks up radio signals.
- Analyzing the Signal: The metal detector’s control box processes the signal received by the search coil. It analyzes the strength and duration of the signal to determine the presence of a metal object. The control box then provides feedback to the user, often in the form of an audible tone and visual display.
Types of Metal Detectors
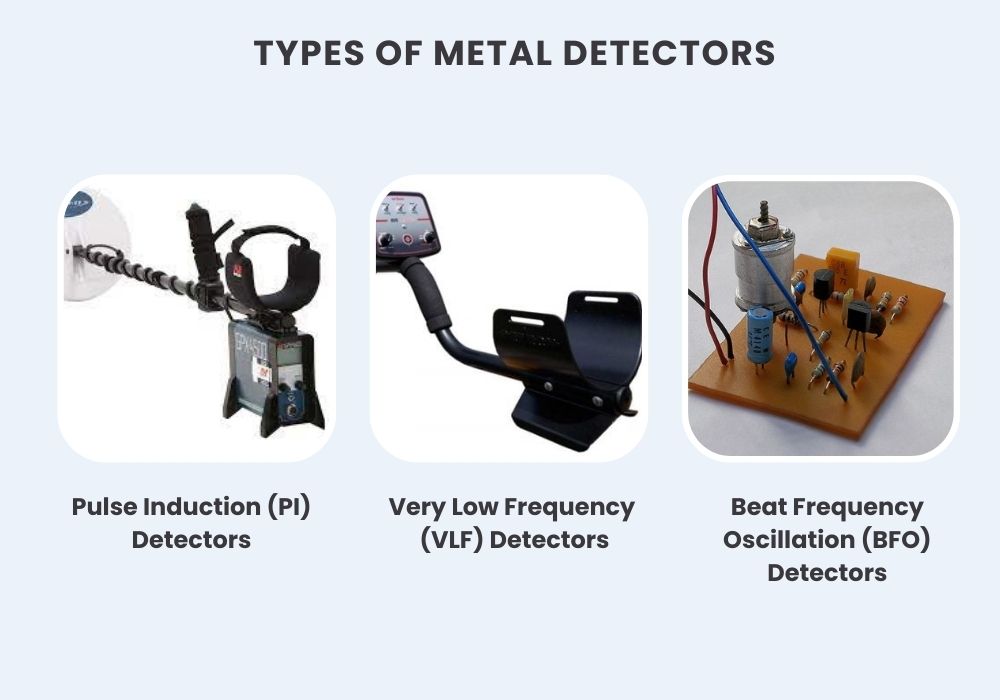
There are various types of metal detectors designed for specific purposes. Let’s explore some common types and their applications:
- Pulse Induction (PI) Detectors: PI detectors are great for finding deeply buried objects and are highly resistant to mineral interference. They are commonly used by treasure hunters searching for valuable relics or by archaeologists on excavation sites.
- Very Low Frequency (VLF) Detectors: VLF detectors are the most common type and are versatile. They are excellent for finding a wide range of metal objects, including coins, jewelry, and relics. Security personnel often use VLF detectors for weapons and contraband screening.
- Beat Frequency Oscillation (BFO) Detectors: BFO detectors are simple and affordable. They are suitable for beginners and can locate larger metal objects, but they lack the precision of other types.
Real-Life Applications of Metal Detectors
Now that we’ve covered the basic principles of Metal Detectors Work and types of metal detectors, let’s explore some real-life examples of how metal Detectors Work.
- Treasure Hunting: Perhaps the most popular use of metal detectors is treasure hunting. Enthusiasts comb beaches, parks, and historical sites in search of lost coins, jewelry, and relics. For example, in 2010, an amateur treasure hunter discovered a hoard of Roman coins in England, dating back to the 4th century.
- Archaeology: Metal detectors play a crucial role in archaeological excavations. They help archaeologists locate buried artifacts, coins, and historical objects without damaging them. In 2012, a metal detectorist discovered the Staffordshire Hoard, the largest hoard of Anglo-Saxon gold and silver metalwork ever found.
- Security and Law Enforcement: Metal detectors are employed at airports, government buildings, schools, and public events to enhance security. They help detect weapons and other prohibited items, preventing potential threats.
- Industrial and Construction: In the construction industry, metal detectors are used to locate buried pipes, cables, and other utilities. This prevents accidents during excavation and construction work.
Advanced Features and Technologies
Metal detectors have come a long way since their inception. Modern models are equipped with advanced features and technologies, enhancing their performance and user experience. Here are some of the innovative features you might find in today’s metal detectors:
- Digital Target ID: This feature provides information about the type of metal detected, helping users discriminate between trash and valuable items.
- Ground Balance: Adjustable ground balance settings help compensate for mineralization in the soil, improving target detection accuracy.
- Pinpoint Mode: Pinpoint mode allows users to precisely locate the target’s position, making it easier to dig and recover the item.
- Wireless Connectivity: Some detectors come with Bluetooth or wireless connectivity, allowing users to pair them with smartphones or headphones for added convenience.
Tips for Successful Metal Detecting
If you’re considering taking up metal detecting as a hobby, here are some essential tips to get you started:
- Research Your Area: Before heading out, research the history of the location you plan to explore. This will give you insights into potential hotspots for finding valuable items.
- Practice with Your Detector: Spend time getting to know your metal detector and its settings. Familiarity with your equipment will increase your chances of success.
- Dig Responsibly: Always obtain the necessary permissions when detecting private property or historical sites. Follow local laws and regulations, and fill any holes you dig.
- Pack Essentials: Bring along essential items such as a digging tool, a finds pouch, and a pinpointer to help you locate and retrieve your targets.
- Join a Community: Joining a local metal detecting club or online forum can provide valuable insights, advice, and camaraderie with fellow enthusiasts.
Conclusions
Metal detectors are incredible devices that have the power to uncover hidden treasures and historical artifacts. Whether you’re a seasoned treasure hunter, an archaeologist, or a security professional, understanding how metal detectors work is essential for success in your endeavors. By harnessing the principles of electromagnetic induction and selecting the right type of detector for your needs, you can embark on exciting adventures or contribute to important discoveries. Just remember to respect the rules and always dig responsibly. Happy hunting!



